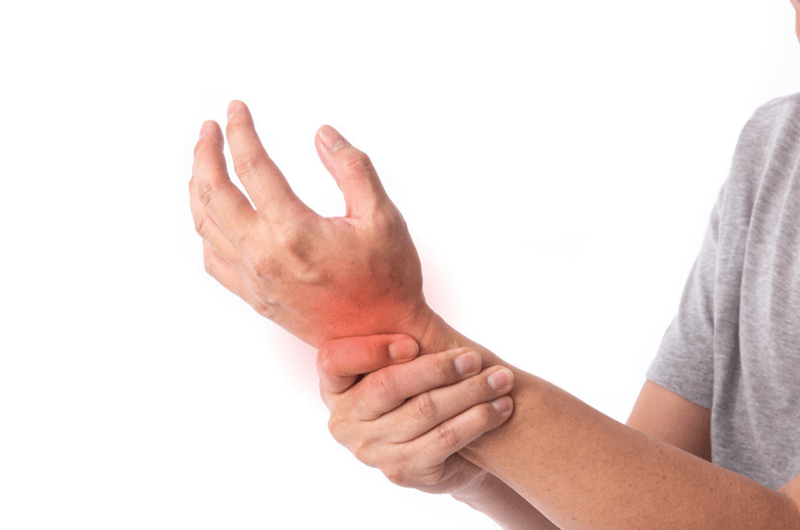
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a common hand and arm condition caused by the compression of the median nerve, a narrow passageway on the palm side of your wrist. The condition, (which usually affects the thumb, index finger and middle finger) is characterized by widespread pain, numbness and tingling sensation in the hand and fingers. Physicians treating this condition must document the diagnosis and medical procedures with accurate medical codes. Outsourcing medical coding can ensure timely and accurate claim submission for optimal reimbursement for the medical services provided.
Generally, a number of factors can directly contribute to this condition. The potential risk factors associated with this condition include – nerve damaging conditions, obesity, strenuous/repetitive work with the hand, family history of CTS, pregnancy – (up to about 50% of pregnant women develop CTS and alterations in the balance of body fluids).
CTS can affect both men and women and the pain symptoms can range from mild to severe. As the intensity of pain increases, it often becomes difficult for a person to hold even a simple object or perform routine manual tasks. Some of the common symptoms include – severe pain in the wrist, palm or forearm, swollen feeling in the fingers, dryness of the skin in the fingers and pain and/or numbness that get worse at night or interrupts sleep.
Diagnosis and Treatment
In most CTS cases, the symptoms get worse over time. For this reason, early diagnosis and treatment are important to avoid permanent damage to the median nerve. Initial diagnosis of this syndrome involves conducting a detailed physical examination along with several diagnostic tests such as X-rays, nerve conduction studies, MRI scan (Magnetic resonance imaging) and electromyogram to determine the correct treatment modality for the same. Treatment modalities include physical therapy, pain management injections, chiropractic care, ice and heat application and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) to reduce pain. However, if the disease symptoms are severe and do not respond to the above mentioned conservative treatment modalities, surgery for CTS will be recommended as a last resort. The surgery relieves pressure by cutting the ligament pressing on the median nerve.
Chiropractic medical coding involves the use of specific ICD-10 codes and CPT codes to document different pain conditions, including carpal tunnel syndrome.
The following medical codes are used –
ICD-10 Codes to Use
G56.0 – Carpal tunnel syndrome
- G56.00 – Carpal tunnel syndrome, unspecified upper limb
- G56.01 – Carpal tunnel syndrome, right upper limb
- G56.02 – Carpal tunnel syndrome, left upper limb
- G56.03 – Carpal tunnel syndrome, bilateral upper limbs
G56.1 – Other lesions of median nerve
- G56.10 – Other lesions of median nerve, unspecified upper limb
- G56.11 – Other lesions of median nerve, right upper limb
- G56.12– Other lesions of median nerve, left upper limb
- G56.13 – Other lesions of median nerve, bilateral upper limbs
CPT Codes to Use
- 20526 – Injection, therapeutic; carpal tunnel
- 29848 – Endoscopic carpal tunnel release
- 64721 – Neuroplasty and/or transposition; median nerve at carpal tunnel
Medical coding for various chiropractic conditions can be challenging process. For accurate and timely medical billing and claims submission, chiropractic practices can outsource their medical coding tasks to an established medical billing company that provides the services of AAPC-certified coding specialists.
A study by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (2018) suggests that musculoskeletal disorders, such as carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) account for 33 percent of all worker injury and illness cases in the United States. There are no foolproof measures that guarantee the prevention of CTS, but several strategies can be adopted to reduce the incidence or risk of developing this common hand and arm condition. Repetitive motion with your wrist is considered one of the biggest risk factors. The simplest prevention measures that can be adopted include reducing repetitive hand movements by alternating between tasks for activities), giving hands and wrists a break from time to time, wearing gloves (to keep hands and wrists warm) and doing regular hand stretching exercises.