Translating treatment and diagnosis information into industry-specific language for billing purposes-or medical coding-is a time-consuming task when performed manually. Thanks to advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence, healthcare providers and medical coding outsourcing companies can leverage computer-assisted coding (CAC) and autonomous medical coding to report diagnoses and treatments for billing purposes. These top-notch tools are designed to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of claim submission, though they cannot replace professional coders.
So, what’s the difference between CAC and autonomous medical coding? CAC software is a tool that coders can utilize to assign medical codes. Autonomous coding takes CAC to a higher level by leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to assign codes without requiring significant human intervention. These sophisticated tools can streamline the work of coders, redirecting their attention from searching and selecting codes to validating the suggested codes provided automatically.
Let’s explore the differences between CAC and autonomous medical coding in greater detail.


Embrace efficiency, accuracy, and compliance with our medical billing and coding services!
Computer-Assisted Coding
CAC combines human expertise and technology to perform medical coding. CAC systems enable medical coders to utilize computer technology for assigning appropriate ICD-10, CPT and HCPCS codes to services documented in healthcare records.
CAC leverages natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) algorithms to analyze. words and phrases within the medical record, cross-referencing them with a diagnostic thesaurus. When a match is identified, the software proposes a code associated with the term to the human coder, who examines the recommended codes, accepts or rejects them, adds any missing codes, and once approved, completes the claim.
For example, consider a patient who underwent a knee replacement surgery. The discharge summary containing detailed information about the procedure, the patient’s condition, and post-operative care is fed into the CAC system. Utilizing NLP, the system will identify key terms, medical conditions, diagnoses, procedures, and services mentioned in the discharge summary and suggest potential medical codes for the knee replacement procedure, associated complications, and follow-up care. The human coder will then review the codes, accept the suggestions, modify them if necessary, or reject them if they believe the CAC system has misunderstood the context. If the coder consistently identifies errors or nuances that the CAC system misses, the system can be updated.
With CAC, the coder reviews the entire chart for complete and accurate code assignment before claim submission. This system significantly accelerates the coding process for the knee replacement surgery, helping coders efficiently translate the complex information from the discharge summary into standardized medical codes. The collaboration between the CAC system and human coders ensures a balance of automation and expertise, ultimately contributing to accurate and timely coding.
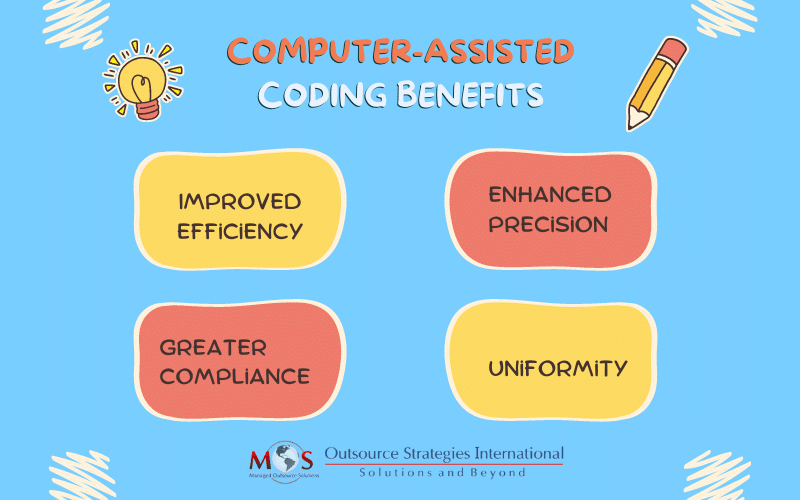
Advantages of CAC
Improved efficiency: The reduction in the average coding time for documents directly translates to increased productivity. Thanks to CAC, manual tasks such as identifying duplicates, sorting documents, code lookup and selection, code ordering, and data entry become either obsolete or can be accomplished at a significantly faster pace.
Enhanced precision: CAC ensures that the output aligns with official guidelines and payer reporting requirements, leading to improved accuracy. This heightened precision results in fewer denials for medical facilities, ultimately contributing to increased profitability.
Uniformity: A key advantage of CAC lies in the consistency it brings to the application of guidelines across various coding resources. The uniformity in the coding process simplifies the analysis of both clinical and financial information.
Greater compliance: CAC promotes accurate coding, reducing the need for additional work time and rebilling. This software’s ability to maintain consistency and accuracy contributes to improved compliance, minimizing the chances of errors and inefficiencies.
Autonomous Medical Coding
Autonomous medical coding involves a higher degree of automation than CAC. Here, coding decisions are made independently by AI systems without requiring significant human intervention. Autonomous coding systems employ ML, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Natural Language Understanding (NLU), or Clinical Language Understanding (CLU) to read and comprehend clinical charts like a human coder. This combination of technologies empowers the system to autonomously process charts, assign accurate codes, continually improve through ongoing feedback, and adapt to coding practices and guidelines.
Autonomous coding can be an optimal choice for coding EKGs or uncomplicated x-rays, notes Find a Code article. These services are frequently conducted hundreds or even thousands of times daily in hospitals. The documentation requirements for these uncomplicated healthcare services are clear and easily identifiable, allowing autonomous coding to swiftly and nearly flawlessly handle them. This, in turn, frees up coders to focus their time on more intricate coding scenarios demanding human intelligence and problem-solving skills.
Benefits of Autonomous Medical Coding
Reduces coding errors: Coding errors can lead to denials, payment delays and increased costs. They can also harm the patient. Mistakes in coding result in regulatory non-compliance, triggering audits from government agencies or insurance payers. Non-compliance could result in financial penalties and reputational damage. Autonomous coding minimizes coding errors.
Ensures strict adherence to standardized coding guidelines: Autonomous medical coding surpasses traditional CAC by independently and consistently applying precise codes. This eliminates the inherent variability linked to human interpretation and ensures strict adherence to standardized coding guidelines.
Speeds up coding process: Crucially, autonomous medical coding significantly expedites the coding process, resulting in quicker diagnosis and shorter wait times for patients. It allows physicians to efficiently managing a substantial caseload in a fraction of the time compared to manual coding or CAC.
Updated with coding guideline changes: With almost immediate updates to guideline changes, autonomous medical coding streamlines practice management. Coding guidelines undergo regular updates, requiring providers to implement changes and retrain their coding teams annually or so. Human coders can find it challenging to keep pace with this continuous adjustment process, leading to an elevated risk of inaccuracies. In contrast, autonomous coding offers a solution by allowing the model to be swiftly configured to reflect updates or modifications to the guidelines.
Improved revenue cycle: As mentioned earlier, automated medical coding is highly accurate. It finds procedures that may be missed by human coders during review, and more precisely determines acuity levels, leading to more accurate diagnoses. Medical coding automation helps patients receive their bills faster, resulting in fewer administrative issues and optimizing the medical billing process.
Human Involvement Still Matters
Both CAC and autonomous medical coding provide notable advantages, significantly increasing efficiency and precision, adherence to coding standards, and strategic allocation of coding resources for optimal outcomes. Even in the face of these advancements, skilled human coders will remain indispensable assets to healthcare organizations in ways that automated systems may not fully replicate. Automation is always missing critical things like modifiers that can be used to get the claim paid. Additionally, certified coders in companies providing medical coding and billing services continually advance their knowledge and expertise, and stay updated on changing codes and standards. Their expertise is indispensable when it comes to leveraging CAC and autonomous coding to streamline documentation processes, enhance patient care outcomes, and ensure accurate reimbursement.