Accurate documentation of any health condition is important from the point of view of patient care as well as timely and correct reimbursement. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) coding is thus an important process in the provider’s office, just as medical coding for various other specialties. Physicians have to utilize the correct diagnostic and procedural codes for arthritis and its treatment. The following diagnostic codes are used to report RA –
- ICD-9-CM – 714.0 – Rheumatoid arthritis
- ICD-10-CM – M06.9 Rheumatoid arthritis, unspecified
Arthritis is one of the most common causes of disability in the United States. About 50 million people in the United States are diagnosed with some form of arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that mainly affects the synovial tissues around the joints. More than 1.5 million people suffer from RA in the United States. Out of every 100,000 people, 41 are diagnosed with this condition every year. Reports suggest that by the end of 2030, the number of people with arthritis is expected to rise to 67 million.
Women are about two and a half times more likely to suffer from this syndrome than men. This disease begins between the ages of 30 – 60 in women and somewhat later in life in men. The lifetime risk for developing this condition is 4% in women and 3% in men. However, RA can occur at any age and even small children can get it. More than 3, 00,000 children in the US have the juvenile form of this disease.
Routine Tests and Diagnosis – Why is it Essential?
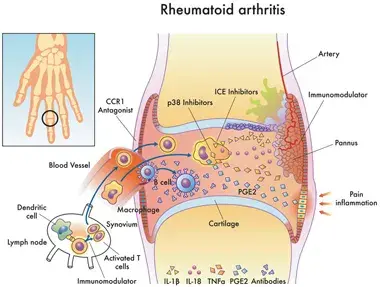
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease that can affect all body parts such as the heart, lungs, tissues, muscles, ligaments and cartilage. The signs and symptoms of this disease may vary in severity and may even come and go. It may also differ from one person to another. Some of the main symptoms include chronic pain, joint swelling and stiffness, fatigue, and weight loss. The potential risk factors associated with this syndrome include heredity, sex, age and lifestyle. Moreover, RA increases the risk of developing other conditions such as stroke, osteoporosis, heart and lung problems, and carpel tunnel syndrome.
Early diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis can help control the disease symptoms and prevent disability. However, it is difficult to diagnose this condition in its early stages as the initial signs and the symptoms mimic those of many other diseases. There is no single blood test or other tests to verify the diagnosis. As part of the physical exam, rheumatologists will check your joints for swelling, redness, reflexes and muscle strength.
These specialists will perform a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation of the disease symptoms by conducting blood tests and X-rays and clearly documenting them. This helps them to better track the progress of this disease in the joints over time.
Anti-inflammatory Drugs Slow Down Bone Loss in Early RA Patients
A recent study found that aggressive anti-inflammatory treatment could reduce the intensity of bone loss in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. The study results show that modern aggressive treatment can minimize osteoporosis in patients with RA.
About 92 patients (mean age – 50.9 years) suffering from RA participated in the research. Out of the total participants, two thirds were women and 80% of them had conducted their bone mineral density assessment at 10 years. These patients experienced disease symptoms for a mean of 12. 4 months. The key findings include –
- Researchers found that about 18.5% of patients with this disease used biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs during the first 2 years of the study.
- On the other hand, 62.6% patients utilized the same drugs for the next 8 years and at the same time the average bone mineral density loss reduced substantially.
- The average yearly rate of bone loss at 2 years and 10 years reduced from -1.00% to -0.56% for the femoral neck, from -0.96% to -0.41% for total spine, and from -0.42% to 0.00% for the L1-L4 vertebrae.