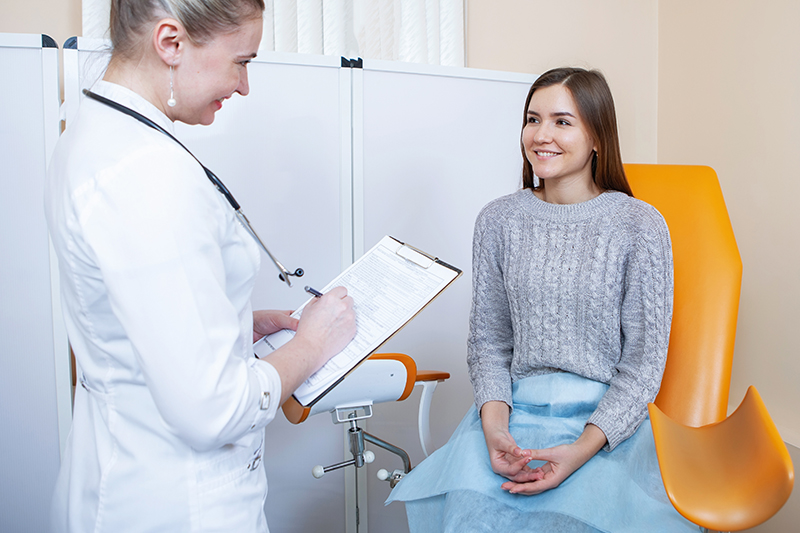
A relatively non-invasive fertility treatment, intrauterine insemination (IUI) involves directly inserting or placing sperm into a woman’s uterus. During a natural conception process, sperms need to travel from the vagina through the cervix, into the uterus, and up to the fallopian tubes. When it comes to IUI, the collected sperms are washed, concentrated and high-quality sperms are placed directly into the uterus. This type of artificial insemination can increase the chances of pregnancy in certain couples who face issues in getting pregnant. Medical billing and coding for this gynecology procedure can be challenging. Relying on the services of professional medical billing companies with solid expertise in this field can help physicians ensure billing and coding efficiency.
Why Is IUI Performed?
When compared to more invasive and costly treatments (such as in vitro fertilization), IUI is a relatively non-invasive and less-expensive fertility treatment. IUIs can be performed with your partner’s sperm or with donor sperm. In certain cases, couples may begin with IUI before progressing to IVF if needed.
Often, IUI is commonly performed in couples who face the following issues-
- Unexplained infertility
- Semen allergy
- Same-sex couples wishing to conceive
- Reduced sperm motility
- Ovulatory factor infertility
- Mild endometriosis-related infertility
- Low sperm count or other sperm impairments
- Issues with the cervix or cervical mucus
- Ejaculation or erection dysfunction
- Donor sperm
- A single woman wishing to conceive
On the other hand, Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) is not effective in certain cases such as women with moderate to severe endometriosis, women who have blockage in both fallopian tubes or have removed both fallopian tubes, women with severe fallopian tube disease, women who have had multiple pelvic infections and men who produce no sperm (unless the couple wishes to use donor sperm). As intrauterine insemination is a relatively simple and safe procedure, the risk of serious complications is low. However, certain risks include infections, multiple pregnancy and vaginal bleeding.
How to Prepare for IUI Procedure
Thetimeline for the IUI procedure is around four weeks (around 28 days) from beginning to end. It is about the same length as a regular menstrual cycle. Before undergoing the IUI process, women need to undergo a thorough medical exam and fertility tests. Their partner will be examined and tested as well. This could include – a uterine exam, ultrasounds of the uterus, a semen analysis, blood tests and screening for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and other infectious diseases. The healthcare provider may recommend taking folic acid (included in most prenatal vitamins) at least three months before conception (or IUI treatment). In certain cases, people are given oral fertility medicine for five days or injectable medication for up to two weeks. This increases their chances of ovulation and releasing multiple eggs. However, not all people require these medications.
State-of-the-art Solutions for your Medical Billing and Coding Needs !
Call Our Experts at (800) 670-2809
Steps Involved in IUI Procedure
Insemination is a quick process, and it takes only a few minutes to insert the sperm. Anesthesia is not required and the procedure is not painful. However, in certain cases, patients may have mild cramping and discomfort during and right after insemination. IUI is often combined with fertility medications that stimulate the ovaries to produce and release as many eggs as possible.
Typically, IUI treatment includes the following steps –
- Ovulation – Determining the timing of ovulation is one of the most important steps in IUI to make sure that the sperm is injected at the right time. This can be done using an at-home ovulation prediction kit that detects luteinizing hormone (LH). Healthcare providers can also detect LH via blood tests. Ovulation typically occurs around 10 to 16 days after the first day of the menstrual period. Insemination (inserting the sperm into the uterus) generally occurs within 24 to 36 hours after LH is detected (in the patient’s blood or urine), or after the hCG injection.
- Semen Sample Preparation – The partner provides a sperm sample on the day of the IUI procedure. In certain cases, the partner can provide the sample at an earlier time and the healthcare provider can freeze it until it is time to be used. On the other hand, when a sperm donor is used, the sample will be thawed and prepared.
- Insemination – As part of the insemination procedure, the healthcare provider will insert a speculum into the vagina. Then, a catheter is inserted through the cervix into the uterus. Finally, the healthcare provider injects the washed sperm sample into the uterus.
Women may be asked to lie down for 10 to 30 minutes after insemination. Physicians may prescribe progesterone after IUI – that helps maintain the lining of the uterus and improve the chances of implantation. Patients may need to take a pregnancy test approximately two weeks after IUI.
CPT Codes for IUI
Billing and coding for IUI involves numerous rules related to reporting the procedure accurately. Physicians administering this fertility procedure must use the relevant CPT codes to bill for the procedure.
The CPT codes for IUI include –
- 58321 or 58322 Artificial Insemination Intra-cervical or Artificial Insemination Intra-Uterine (codes can be used interchangeable but not to exceed 2)
- 58323 Sperm Washing for Artificial Insemination (codes can be used interchangeable but not to exceed 2)
- 76830, 76856, 76857 Ultrasound, Transvaginal (codes can be used interchangeable but not to exceed a total of 6)
- 82670 Estradiol
- 83001 Gonadotropin- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (fsh)
- 83002 Gonadotropin- Luteinizing Hormone (lh)
- 84144 Progesterone
- 84702 Gonadotropin, Chorionic (hcg) – Quantitative
- 99211 Office or other outpatient visit for the evaluation and management of an established patient that may not require the presence of a physician. Usually, the presenting problem(s) are minimal. Typically, 5 minutes are spent performing or supervising these services.
- 99212 Office or other outpatient visit for the evaluation and management of an established patient, which requires at least 2 of these 3 key components
- 89253 (AH) Assisted Embryo Hatching, Micro techniques (any method)
- 89258 Cryopreservation; embryos
- 89342 Storage, (per year); Embryo(s)
- 89337 Cryopreservation, Mature Oocytes (eggs)
- 89352 Thawing of Cryopreserved; Embryo(s)
- 89290, 89291 Biopsy, Oocyte polar body or embryo blastomere, micro technique (PGD and/or PGS)
As mentioned above, intrauterine insemination is a relatively low-risk treatment that can be a great option for many women trying to conceive. The success of the IUI procedure varies depending on the underlying cause of infertility. Crucial factors include the cause of infertility, the woman’s age, the man’s sperm count and sperm quality, and whether fertility medicines are used to stimulate ovulation. In fact, IUI works best in people with unexplained infertility, and people with cervical mucus issues or issues with ejaculation.
Associate with OSI for your medical billing and coding needs!
Schedule a free consultation with our experts – call (800) 670-2809
Obstetrics and Gynecology medical billing and coding can be complex. Outsourcing medical billing tasks to professional companies can help providers submit accurate claims. Reputable billing and coding companies offer the services of expert coders who are well-informed in the latest coding and billing guidelines.