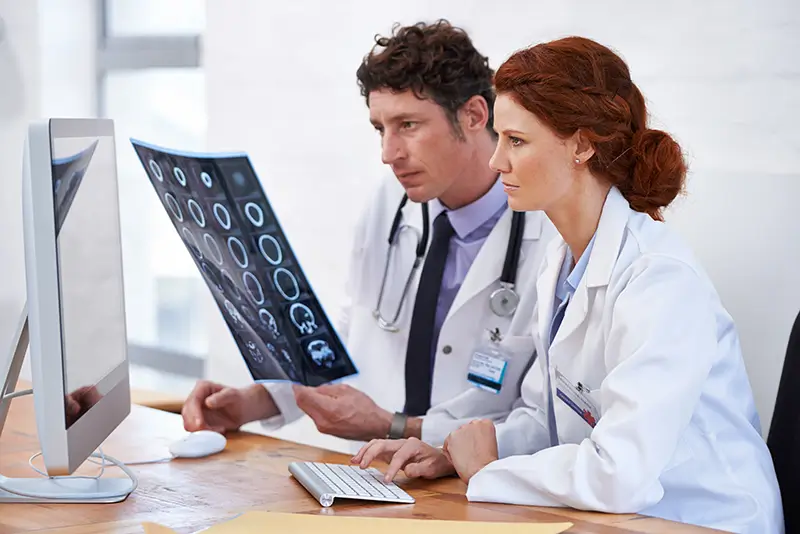
Radiologists perform both interventional and non-interventional/non-invasive procedures. Interventional radiology procedures include diagnostic radiology imaging and ultrasound, while non-interventional procedures comprise standard radiographs, single or multiple views, contrast studies, computerized tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
Accurate radiology medical billing is essential for ensuring healthcare providers receive proper reimbursement for the diagnostic imaging services they provide to patients. To get proper reimbursement for the procedures they perform, radiologists need to execute proper disease and diagnosis coding or ICD-10 coding (using three-digit codes that are modified by including a fourth or fifth digit as characters following a decimal point), and procedural coding using Current Procedural Terminology (CPT), comprising 5 digits with 2-digit modifiers. The procedure will be considered medically necessary only with a supporting ICD-10 diagnostic code. Sometimes multiple codes, such as radiological and surgical codes may become necessary to report a full procedure.


Boost your practice’s revenue cycle with our comprehensive radiology medical billing services!
Radiology Medical Billing Strategies – Overview
Patient registration and verification
- Collect patient demographic and insurance information accurately
- Verify insurance coverage and eligibility for radiology services
Documentation and coding
- Review radiology reports and medical records
- Assign appropriate CPT codes and ICD codes for billing
Claims preparation and submission
- Compile all necessary documentation
- Submit claims electronically to insurance companies
Claims processing and adjudication
- Monitor claims status and track for timely processing
- Handle any claim rejections or denials promptly
Payment posting and reconciliation
- Post payments received from payers into the billing system
- Reconcile payments with billed amounts to ensure accuracy
Denial management and appeals
- Investigate and resolve claim denials promptly
- Prepare and submit appeals for denied claims
Patient billing and follow-up
- Generate patient statements and invoices
- Follow up with patients regarding unpaid balances
Understanding Radiology Codes
CPT Codes
Radiology CPT codes are subdivided on the basis of the type of service and anatomical site.
Diagnostic Radiology 70010 – 76499
Diagnostic Ultrasound 76506 – 76999
Radiologic Guidance 77001 – 77022
Breast, Mammography 77046 – 77067
Bone/Joint Studies 77071 – 77086
Radiation Oncology 77261 – 77799
Nuclear Medicine 78012 – 79999
Interventional radiologists use certain surgical codes to signify the procedures they perform. Some major surgical codes include the following:
- Mechanical Thrombectomy: 37184
- Biliary Drainage: 47533
- Cholecystostomy Tube Placement: 47490
- IVC Filter Placement: 37191
- Biliary Stone Removal: 47544
HCPCS Codes
Medical services and supplies that are not included in the CPT coding terminology are listed in the HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System procedural codes). These are represented by 1 letter (from A to V) followed by four digits. Numeric or alphanumeric modifiers can be used along with these codes to clarify a procedure.
Modifiers
Radiological service can be billed for the physician’s work as well as the use of equipment or supplies. The technical component (TC) includes facility charges, equipment, supplies, pre-/post injection services, staff and so on. The professional component (PC) involves studying and making inferences about the radiological test and submitting a written report with the findings. Modifiers are used to signify the technical and professional components in a radiological service. They are 2-digit numbers that are used to explain a procedure in more detail. They can indicate repeat or multiple procedures, such as radiographs performed bilaterally.
- When billing for the technical component only, the modifier 52 has to be used; when billing only for the professional component, the modifier 26 is to be used.
In the latter case, a written report by the physician providing the services is required to avoid claim denial.
Some other examples of modifiers are: -TC, -26, -TC and -26 combined, -52, -59, -76, – 77. -LT, -RT, -E1 to -E4, -TA to -T9, -FA to –F9, and -LA are – anatomical modifiers.
Billing for Professional Component
Physicians can bill for the professional component of radiology services provided for an individual patient in all settings regardless of the specialty of the physician who performs the service. Reimbursement will be given under the fee schedule for physician services. However, for radiology services provided to hospital patients, insurance carriers reimburse the professional component only under the following conditions:
- Services should meet the fee schedule conditions
- Services provided should be identifiable, direct and discrete diagnostic or therapeutic services given to an individual patient
Payment for the Technical Component
As regards the technical component or TC of radiology services furnished to hospital patients and to Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) inpatients during a Part A covered stay, insurance carriers might not provide reimbursement. The fiscal intermediary (FI)/AB MAC makes the payment for the administrative/supervisory services offered by the physician, as well as for the provider services. The TC of radiology services offered for inpatients in hospitals, excluding CAHs or Critical Access Hospitals are included in the FIs/AB MAC payment to hospitals. In the case of hospital outpatients, radiology and related diagnostic services are reimbursed according to the Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS) to the hospital. In the case of a SNF, the radiology services offered to its inpatients will be included in the SNF Prospective Payment System (PPS). For services offered for outpatients in SNFs, billing can be made by the provider of the service or by the SNF according to arrangements made with the provider. When the billing is made by the SNF, Medicare reimburses in accordance with the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule.
Radiology Billing Standards
Radiology services can be billed in a number of ways. Some of the services are split billable and the codes for these are separately reimbursed by different providers for the professional and technical component. The physician and the facility can bill for their respective component with modifiers 26, TC or ZS. In full fee billing, the physician bills for both the professional and technical components and makes the payment due to the facility for the technical component provided. In standard billing, the facility bills for both the professional and technical components and reimburses the physician for his professional component. Services that cannot be separately billed are not individually reimbursed for the professional or technical components. These codes are reimbursed only for one provider and must not be submitted with the 26, TC or ZS modifiers.

Professional Coding Services for Accurate Billing and Coding
When it comes to coding, the radiologist faces two main issues: first, understatement of completed treatment could mean insufficient reimbursement; second, if the codes overstate the treatment, it could result in risk of abuse, repayments and fines. Another problem is the complicated and ever-changing directives with regard to CPT procedures.
Coding Skills Required
The following skills are essential for accurate coding and billing for radiology services:
- Ability to review clinical issues and CPT, ICD-9 and HCPCS coding guidelines for interventional and non-interventional radiology
- Knowledge about the differences between diagnostic radiology codes and therapeutic interventional radiology codes
- Skill to review coding guidance for modifier usage with interventional radiology procedures
- Ability to code challenging case scenarios
Radiologists can resolve all these issues by going in for the services of professional medical coding companies. They have skilled CPT coders to do the job. With great attention to detail, in-depth knowledge of the coding system, application of basic coding principles, and thorough documentation, these companies offer accurate, customized and affordable radiology medical billing and coding services in quick turnaround time. Professional companies use state-of-the-art billing software to guarantee efficiency and accuracy in billing and coding, for checking local coverage determination and so on and ensure that all claims are reimbursed.