Foot deformities are structural abnormalities or muscular imbalances that affect the function of the foot. There are many different types of foot deformities. While some foot disorders may be present from birth, others can occur over time. Podiatrists treating foot disorders can consider medical coding outsourcing to get their services accurately reported on medical claims for on-time reimbursement.
To diagnose such conditions and to check for joint damage and bone alignment, podiatrists may perform a physical examination or use X-rays. Treatment options depend mainly on the type and severity of the deformity. Often, foot orthotics and manipulative treatments are recommended for correctable foot deformities, while surgical correction may be required for resistant foot deformities.
ICD-10 Codes for Common Foot Deformities
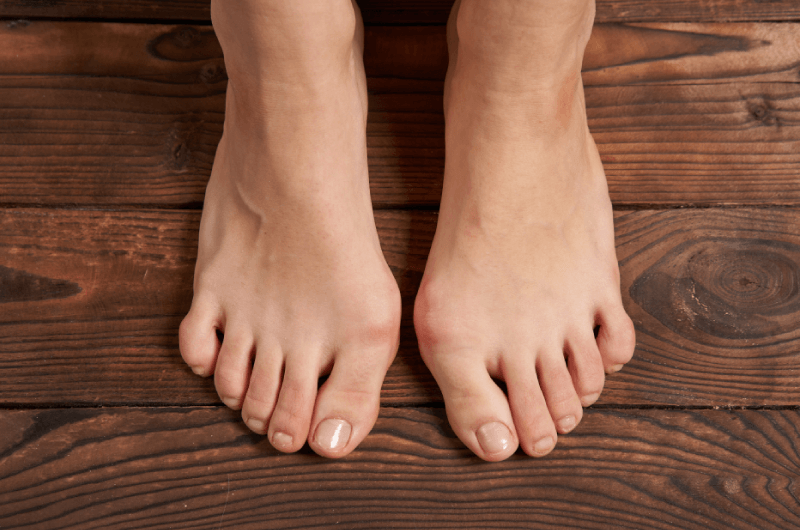
Bunions (Hallux Valgus)
Bunions refer to the bump on the outside of the big toe, causing discomfort or pain. It can be caused by the pressure from the way one walks, abnormal movement of the joints, or because of the foot shape. Treatment options include physical therapy, orthotic devices, pain medications, injections, or surgery.
- M20.10 …… unspecified foot
- M20.11 …… right foot
- M20.12 …… left foot
Blisters
Walking or standing for several hours a day or using poorly fitted shoes puts pressure on the heels, soles, and toes, causing feet blisters. These fluid-filled bubbles or pockets can also be the result of excessive moisture or sunburn. Blood blisters include raised sections of skin filled with blood. Treatment for blisters includes applying an ice pack, using blister bandages to cover the affected area, and applying antibiotic ointments or creams. Diabetic people experience occasional blisters on their skin.
- S90.82 Blister (nonthermal) of foot
- S90.821 Blister (nonthermal), right foot
- S90.821A …… initial encounter
- S90.821D …… subsequent encounter
- S90.821S …… sequela
- 822 Blister (nonthermal), left foot
- S90.822A …… initial encounter
- S90.822D …… subsequent encounter
- S90.822S …… sequela
- S90.829 Blister (nonthermal), unspecified foot
- S90.829A …… initial encounter
- S90.829D …… subsequent encounter
- S90.829S …… sequela
- S90.821 Blister (nonthermal), right foot
Hammertoe
This foot deformity causes the toe to bend at the middle joint, instead of pointing forward. If left untreated, this condition may require surgery. It can be caused by muscle imbalance and the symptoms may include difficulty in walking, swelling, redness, and more. Surgical treatments such as tendon lengthening, tendon transfer or joint fusion may be recommended, depending on the type and extent of the deformity.
- M20.4 Other hammer toe(s) (acquired)
- M20.40 …… unspecified foot
- M20.41 …… right foot
- M20.42 …… left foot
Athlete’s Foot
This contagious fungal skin infection occurs between the toes mainly due to sweat accumulating within tight-fitting shoes. Common symptoms include burning, itchiness, cracked skin between toes, blisters, or dry and scaly skin. This condition is mainly treated using over-the-counter (OTC) topical antifungal medications, topical steroid medications, or oral antibiotics. Leaving this condition untreated can result in the infection spreading to the toenails.
- B35.3 Tinea pedis
Flatfoot (Pes Planus)
This is a common disorder when the entire sole of the foot is in contact or near contact with the ground while standing. Two common types of flatfoot are – flexible and rigid flatfoot. Flexible flatfoot or pediatric flatfoot is first apparent in childhood, while a rigid or adult acquired flatfoot develops in adults. Foot pain or leg discomfort can be treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), heat, or massage. If the disorder is related to another condition, surgery or other treatment will be recommended.
- M21.4 Flat foot [pes planus] (acquired)
- M21.40 …… unspecified foot
- M21.41 …… right foot
- M21.42 …… left foot
- Q66.5 Congenital pes planus
- Q66.50 …… unspecified foot
- Q66.51 …… right foot
- Q66.52 …… left foot
High arch feet (Pes Cavus)
Pes cavus or high arch is a common foot deformity in which the arch of the foot (the area between the heel and the ball of the foot) is high. High arch feet may cause many problems such as occasional discomfort or permanent skeletal issues. Diagnosing cavus foot deformity involves taking X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nerve conduction study, or electromyography.
- Q66.6 Other congenital valgus deformities of feet
- Q66.7 Congenital pes cavus
- Q66.70 …… unspecified foot
- Q66.71 …… right foot
- Q66.72 …… left foot
Corns and Calluses
Most often seen on the feet and toes, corns and calluses are thick, rough areas of skin or a hardened bump. While calluses are formed, as the result of the skin hardening due to excessive pressure, and don’t cause any pain, corns form a hard lump surrounded by inflamed skin in one area and are very painful.
- L84 Corns and callosities
The need to use modifiers and the difficulty of coding complex inclusive procedures and other challenges often make podiatry medical billing complex.
To address such complexities, medical practices can consider the support of an experienced medical billing and coding company like Outsource Strategies International (OSI) to deal with claim submission and follow-ups. Professional billing and coding teams will be up-to-date with the complex rules and guidelines to evaluate podiatry claims.