In the complex landscape of healthcare reimbursement, medical billing codes and standards offer healthcare professionals a uniform language for coding diagnosis and medical services and procedures. The primary medical coding classification systems for managing medical billing in the United States are ICD-10-CM, ICD-10-PCS, CPT and HCPCS Level II. Understanding these codes is essential for healthcare providers to streamline their billing processes, ensure accurate claim submission and reimbursement, and comply with regulatory requirements. With the intricacies involved, most providers rely on professional medical billing services to streamline reporting, and increase accuracy and efficiency.
Medical Billing Codes – Types and Applications
ICD-10, CPT and HCPCS medical billing codes play an essential role in the medical billing process.
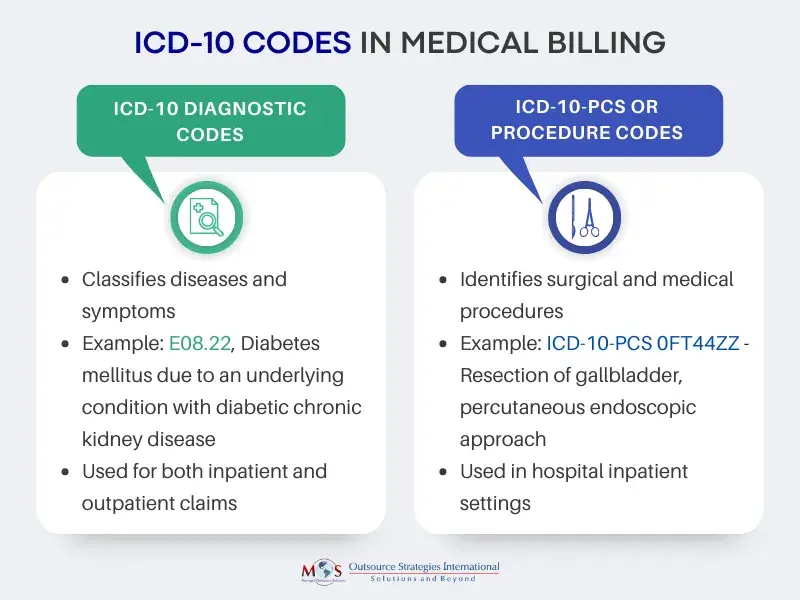
ICD-10 Codes in Medical Billing
ICD-10 codes primarily represent diagnoses and the patient’s ailments, illnesses, or injuries, helping to justify the medical necessity of the services provided. These codes are diverse and detailed, covering various aspects of conditions, including complications and connections to other health issues. This specificity poses challenges for insurance reimbursement.
Compared to ICD-9, ICD-10 codes provide more detailed information in a seven-character, alphanumeric format. The first digit of an ICD-10 code is a letter (alpha), the second digit is numeric, and the third to seventh digits may be alpha or numeric.
- The first three characters represent the type of disease or health condition. Codes longer than 3 characters always have decimal point after first 3 characters.
- Characters 4-6 (numeric or letter) provide more details like etiology, anatomic site, severity, or other clinical details.
- Character 7 (letter) – extension. The seventh character signifies the type of encounter (“initial encounter,” “subsequent encounter”, and “sequela”).
Each additional character in the ICD-10 code represents greater diagnostic information. Physicians should code diagnoses to the highest level of specificity available in the ICD-10 code set.
There are two ICD-10 code sets: ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS. ICD-10-CM represents the diagnosis code set used for all healthcare settings and ICD-10-PCS represent the procedure code set used only in hospital inpatient settings.
ICD-10 Codes
Thorough clinical documentation of patient conditions is necessary for coders to assign precise ICD-10 codes in medical billing. Medical coding experts meticulously analyze clinical documentation to assign codes with the utmost specificity, aiding in insurance reimbursement.
When submitting medical claims to payers, ICD-10 codes are used together with CPT codes to paint a complete picture of a patient’s encounter.
CPT Codes in Healthcare
CPT stands for Current Procedural Terminology—the code system created by the American Medical Association (AMA). According to the AMA, the aim of CPT codes in healthcare is to offer a “uniform language for coding medical services and procedures to streamline reporting, increase accuracy and efficiency”.
While ICD-10 codes justify services provided by detailing the patient’s diagnoses and demonstrating the medical necessity of the rendered services, CPT codes describe the procedures, services, and treatments performed by healthcare providers.
The CPT medical code set is used to report evaluations, diagnostic procedures, surgeries, and services provided by healthcare professionals to patients. Most healthcare professionals rely on outsourced medical billing services to report the correct CPT codes and receive appropriate reimbursement for their services and avoid audits.


Streamline your billing process and boost your practice’s financial health with our medical billing services!
CPT Code Categories
The CPT code set contains thousands codes and is updated every year. There are three types of CPT codes: Category 1, Category 2 and Category 3.
- Category I: Procedures, services, devices, and drugs (including vaccines)
- Category II: Performance measures and quality of care
- Category III: Services and procedures using emerging technology
Category I CPT codes in medical billing are classified into six sections:
- Evaluation and Management
- Anesthesia
- Surgery
- Radiology
- Pathology and Laboratory
- Medicine
Category II CPT codes comprise four-digit numbers followed by the letter F. They complement Category I codes by serving as tracking and performance indicators. Health providers utilize these codes to document therapeutic, preventive, or other interventions, including follow-up care and various aspects of a patient’s medical history.
Category III codes, characterized by a four-digit number with the letter T, are temporary codes that allow data collection for emerging technologies, services, and procedures. They are used to report procedures that do not have a Category I code. Once their effectiveness is substantiated, often through FDA approval, these innovative procedure codes achieve Category I status.
Level II HCPCS Codes
HCPCS codes are a separate set of codes used to describe non-physician services such as drugs, supplies, and certain other services not included in CPT. Coders use HCPCS codes to submit claims for medical procedures to Medicare, Medicaid, and several other third-party payers.

Check out our blog post to gain insights into CPT codes in medical billing
Modifiers in Medical Billing
CPT and HCPCS Level II codes have modifiers that provide additional information about the medical procedure, service, or supply without changing the code that applies. A medical coding modifier has two characters which can be alphanumeric or numeric. Situations in which modifiers are used include:
- The service or procedure has both professional and technical components.
- More than one provider performed the service or procedure.
- More than one location was involved.
- A service or procedure was increased or reduced in comparison to what the code typically requires.
- The procedure was bilateral.
- The service or procedure was provided to the patient more than once.
Using CPT modifiers correctly is necessary to receive accurate reimbursement for medical services.

Read our blog post on Navigating Modifier Codes for Precise Billing to discover how to enhance your billing precision.
HIPAA Compliance in Medical Billing
HIPAA compliance in medical billing is paramount for safeguarding patient information. It ensures that all billing processes and systems adhere to the standards set by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This federal law mandates strict protocols to protect the privacy, security, and confidentiality of patients’ protected health information (PHI).
Covered entities include healthcare providers, health insurance companies, and clearinghouses as well as their business associates such as medical billing outsourcing companies, EHR vendors, and other third party service providers handling PHI on behalf of covered entities.
HIPAA compliance necessitates that medical billing services establish safeguards to protect patient data, train staff on privacy and security practices, and maintain strict confidentiality throughout the billing cycle. Compliance involves:
- Secure handling of data
- Restricted access to patient records
- Encryption of sensitive information
- Staff training on privacy practices, and
- Maintaining audit trails to track data access
Adhering to HIPAA guidelines not only mitigates the risk of data breaches but also fosters trust between patients, healthcare providers, and insurers, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive medical information.
Significance of Accurate Medical Billing for Financial Health
Accurate medical billing boosts the financial health of your healthcare practice in many ways:
- Maximum reimbursement: supports fast and correct reimbursement
- Minimizes revenue loss: prevents claim rejections or underpayments or payment delays.
- Promotes compliance: ensures compliance with HIPAA and Medicare guidelines, reducing risk of audits, fines, or penalties
- Improved operational efficiency: streamlines billing processes, leading to efficient revenue cycles
- Improved financial analysis, tracking and planning: provides reliable data for financial reporting and analysis, improving financial decision-making
- Patient satisfaction: contributes to a positive reputation and patient satisfaction.
Check Out Our Infographic on Medical Billing Codes

Ensure accuracy, compliance, and optimal reimbursement with our customized medical billing and coding services.
Leveraging professional coding and medical billing services is the best option to correctly code and bill services rendered. Experienced AAPC certified coders stay on top of the rules of CPT coding and will ensure that you assign codes to the highest level of detail and specificity.